Photoluminescence (PL) Imaging
Photoluminescence (PL) imaging is a diagnostic technique used to assess the quality and performance of solar photovoltaic (PV) modules by examining the light emitted from the solar cells when they are excited by an external light source. This method is particularly useful for evaluating the material properties and identifying defects in the semiconductor layers of solar cells.
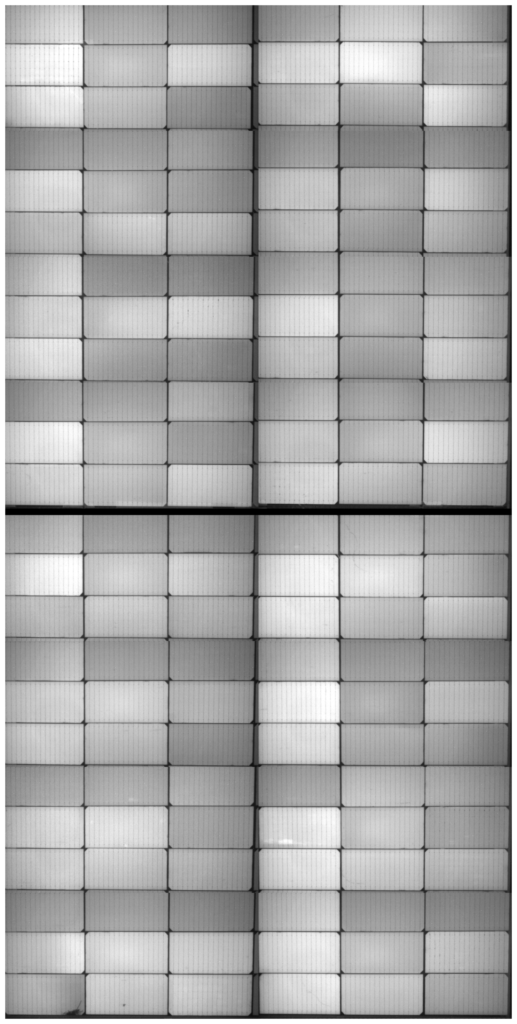

How PL Imaging Works
- Light Excitation:
An external light source, typically a laser or high-intensity LED, illuminates the solar cells. This light excites electrons in the semiconductor material, causing them to emit light (photoluminescence) as they return to their ground state.
- Image Capture:
A sensitive camera, often a CCD or CMOS camera, captures the emitted light. The intensity and wavelength of the emitted light provide information about the quality and uniformity of the semiconductor material.
- Analysis:
The PL image is analyzed to identify variations in light emission, which indicate different types of defects and inhomogeneities. Bright and dark regions correspond to areas with varying levels of material quality and performance.
Types of Defects Detected by PL Imaging
- Material Inhomogeneities
- Recombination Centers
- Microcracks and Grain Boundaries
- Impurity Clusters
Advantages of PL Imaging
- Non-Destructive
- High Sensitivity
- Detailed Material Analysis
Applications of PL Imaging
- Material Development
- Manufacturing Quality Control
- Performance Optimization